

Since a stator and its winding of three phase induction motor is the same as that of a synchronous motor.

It will start rotating in reverse direction and so does the rotor. If we interchange any two phases of the AC supply, we will get new phase sequence, then the direction of rotating magnetic field in three phase induction motor will reverse. To reduce the speed of the rotating magnetic field of the stator to a low enough value that the rotor can easily accelerate and lock in with it during one half. The direction of rotating magnetic field depends upon the phase sequence of the AC supply connected across the stator winding. The magnetic field in three phase induction motor (RMF) rotates at a constant speed called synchronous speed (Ns), which is given by, Speed of Rotating Magnetic Field in Induction Motor The phasor diagram for θ =180 o is shown in Figure (d). Similarly we can prove that ɸ T at θ =180 o is given by, Here is how the Synchronous Speed calculation can be explained with given input values -> 2700 (12090)/(4).
#Possibl values of synchronous speed ns how to
How to calculate Synchronous Speed using this online calculator To use this online calculator for Synchronous Speed, enter Frequency (f) & Number of Poles in an Electrical Machine (P) and hit the calculate button. all the angles are drawn with respect to this phasor. Synchronous Speed is denoted by Ns symbol. We will use the phasor ɸ R as the reference phasor i.e. In other words ɸ T rotates in the clock wise direction. Step 2: For every value of θ in step 1, we will draw the phasor diagrams.īy observing these phasor digrams you can understand easily that ɸ T keep shifting its position from 90 o to 30 o to – 30 o to – 90 o and so on. Step 1: We will find the values of total flux ɸ T for different values of θ such as 0, 60, 120, 180 …. To prove that this RMF is rotating we will: Therefore, ɸ T = ɸ R + ɸ Y + ɸ B Prove that RMF in Induction Motor is Rotating The effective or total flux (ɸ T) in the air gap is equal to the phasor sum of the three components of fluxes ɸ R, ɸ Y and, ɸ B. Mathematically, they are represented as follows: torque value C, it is thus possible, from knowing the slip g of the motor 10 for a. Let the flux produced by the line currents I R, I B, I Y be φ R, φ B, φ Y respectively. These curves show that for the same value of synchronous speed Ns. If Ns and Nr being the synchronous speed of rotating magnetic flux and rotor speed. The value of slip in induction motor is can never be zero. These fluxes have the same frequency as that of the line currents, and they also have the same phase difference of 120 o with respect to each other. Slip in Induction Motor is the relative speed between the rotating magnetic flux and rotor expressed in terms of per unit synchronous speed. Due to each line current, a sinusoidal flux is produced in the air gap. These line currents have phase difference of 120 o with respect to each other. Whenever the AC supply is connected to the stator windings, line currents I R, I Y, and I B start flowing. The stator has a three phase stationary winding which can be either star connected or delta connected. If the Greek symbols for alpha beta delta do not appear here the symbol font needs to be installed for correct display of notation and formulae.The induction motor rotates due to the rotating magnetic field in induction motor, which is produced by the stator winding in the air gap between the stator and the rotor. The symbol font is used for some notation and formulae.
#Possibl values of synchronous speed ns generator
The field excitation of an isolated synchronous generator determines its output voltage.
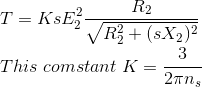
The output power P m for a load torque T m is: The synchronous rotational speed n s and synchronous angular speed w s of a machine with p pole pairs running on a supply of frequency f s are:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
